암 유전자 RAS와 RhoA는 이상적인 동반자로 작용하며, RhoA가 계획된 세포사멸(apoptosis)을 막아내어 암세포가 죽지않고 살아남는 동안, RAS는 암세포의 성장을 강화시킵니다. 양쪽 모두 자연치료제 조르반(Zorvan), 씨놀짐(SinnolZym), 지놀짐(GinolZym), 루테올린(luteolin)을 비롯해 스태틴(statin)계 약물과 좀메타(Zometa)와 액토넬(Actonel)같은 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates)계 약물을 통해 억제가 가능하다고 앞에서 설명드렸습니다.
아래 연구보고는 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 계 약물의 항암작용에대해 주로 다루었으며, 콜레스테롤 합성경로에서 스태틴(statin)계의 약물과 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 계 약물의 작용에 대해 잘 설명합니다. 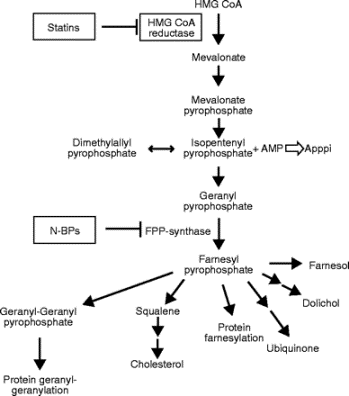 좌측의 도표를 보면 콜레스테롤(Cholesterol) 등을 생합성하는 메발로네이트 경로(mevalonate pathway)에서 스태틴(statins)계 약물은 HMG-CoA 환원효소를, 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates: N-BPs)는 뼈를 분해하는 역할을 하는 파골세포 기능에 중요한 효소인 FPP (Farnesyl pyrophosphate) 합성효소(synthase)를 강력하게 억제하는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 골다공증 치료제인 비스포스포네이트(bisphosphonates)는 여러 경로에 작용하여 골흡수를 억제하는 작용이 강하므로 특히 유방암, 전립선암, 폐암을 비롯해 뼈로 전이가 잘 되는 암 치료 시 전이 및 뼈분해를 억제하는데 자연치료제와 함께 사용될 수 있습니다.
좌측의 도표를 보면 콜레스테롤(Cholesterol) 등을 생합성하는 메발로네이트 경로(mevalonate pathway)에서 스태틴(statins)계 약물은 HMG-CoA 환원효소를, 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates: N-BPs)는 뼈를 분해하는 역할을 하는 파골세포 기능에 중요한 효소인 FPP (Farnesyl pyrophosphate) 합성효소(synthase)를 강력하게 억제하는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 골다공증 치료제인 비스포스포네이트(bisphosphonates)는 여러 경로에 작용하여 골흡수를 억제하는 작용이 강하므로 특히 유방암, 전립선암, 폐암을 비롯해 뼈로 전이가 잘 되는 암 치료 시 전이 및 뼈분해를 억제하는데 자연치료제와 함께 사용될 수 있습니다.
Bisphosphonates: preclinical review.
Bisphosphonates: clinical experience.
여기에서 유념할 것은 비스포스포네이트계 골다공증치료 약물들이 모두 같지 않다는 것입니다. 클로드로네이트(Clodronate) 같은 오래된 약물은 항암능력이 없습니다. 오직 질소-비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 약물만이 항암작용을 합니다. 왜냐하면 특히 RAS, Rho와 결합하는 지질(lipid)을 만드는 효소FPP의 합성을 이 약물이 억제하기 때문입니다. 이 지질(lipid)변화는 세포막내피에서 이들 분자들을 다른 분자들과 상호 반응하게 허용하며, 그리하여 잠재된 암 성장요인들을 활성화 시킵니다..
가장 잠재효능이 높은 질소-비스포스포네이트 약물은 아마도 좀메타(Zometa) 또는 졸레드로닉산(zoledronic acid) 일 것입니다. 다음이 액토넬(Actonel) 또는 라이즈드로네이트( risedronate) 입니다. 스태틴계약물과 질소-비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates)골다공치료약물이 암유전자 RAS와 RhoA가 활성화 되는 것을 차단하며, RAS를 차단하는 것은 암세포성장의 주요경로를 차단하는 것이며, RhoA를 억제하는 것은 암세포를 항암약물에 매우 민감하게 만듭니다. 그렇다면 우리의 주요한 관심은 미세한 유전자 단백질 RAS와 RhoA를 중화시키는데 있으므로, 질소 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 약물만으로 이 목표가 달성될 수 있을 것 같은데, 대체 어째서 자연치료제 조르반(Zorvan), 씨놀짐(SinnolZym), 지놀짐(GinolZym), 루테올린(luteolin)을 비롯해 스태틴(statin)계 약물의 사용을 함께 하는지 의아할 것입니다.
이것이 한 가지 이유입니다. 다음 연구보고에서는 스태틴(statin)계 약물로는 합성이 차단될 수 있으나 질소 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 약물로는 합성을 차단할 수 없는 물질 옥시스테롤(oxysterol: 콜레스테롤 대사의 분해산물)이 유방암세포에서 이동을 유발하는 요인으로 작용한다는 것을 발견하였습니다. 이 물질은 확실히 정상적인 뼈에서 충분한 양이 만들어지며, 혈액으로 분비됩니다. 옥시스테롤(oxysterol)은 화학주성인자(chemotactic factor)처럼 전이성 유방암세포가 자리잡고 증식할 수 있는 뼈로 보내는 작용을 매개하고, 결국 골 기질(bone matrix)을 파괴하게 됩니다. 예전에는 이러한 연구보고가 없습니다. 유방암, 전립선암, 폐암 세포는 뼈로 전이되기 쉬우나, 그 이유를 아무도 몰랐습니다. 왜 뼈로가는가?
이제 이것이 드러나서 옥시스테롤(oxysterol)이 뼈에서 많은 양이 만들어지고 배출되며, 뼈에서 중요한 기능을 하는 것으로 보입니다. 전립선암 세포와 폐암 세포의 옥시스테롤(oxysterol)에 대한 반응 역시 조만간 밝혀질 것입니다. 또 다른 연구보고는 정상적인 뼈를 만드는 조골세포(osteoblast)에서 암의 성장과 분화(differentiation)에 관여하는 중요한 성장인자인 TGF-beta1 (Transforming growth factor-beta1)의 발현을 증가시키고, 결과적으로 암세포의 전이에 관여하는 단백질 인테그린 베타1과 베타3 (beta1 and beta3 integrins)를 활성화시켜 유방암세포의 전이가 촉진된다는 결과를 보여줍니다.
스태틴(statin)계 약물은 TGF-beta1의 발현 역시 억제하므로, 그 결과 혈관신생(angiogenesi) 역시 억제됩니다. 또한 TGF-beta1의 발현을 억제하는 것은 파이토스테롤(phytosterol)이며, 우리가 사용하는 자연치료제 조르반(Zorvan), 씨놀짐(SinnolZym) 정제와 액체, 지놀짐(GinolZym), 오랄짐(OralZym) 등에는 특정 식물에서 추출된 각기 다른 종류의 파이토스테롤(phytosterol)이 사용됩니다. 특정 식물의 스테롤(plant sterol)은 인체의 콜레스테롤과 매우 유사한 구조이지만 작용은 크게 다릅니다.
따라서 유방암, 전립선암, 폐암 환자는 뼈로 전이가 되는 것을 예방하는 차원에서 이러한 치료제들을 복용해야 합니다. 암이 일단 뼈로 들어가면 치료가 매우 어려워지며, 뼈의 파괴와 심한 통증이 생기게 됩니다. 우리는 뼈로 전이가 되는 것을 차단하기 위해 가능한 모든 수단을 강구해야 합니다. 자연치료제나 스태틴계 약물, 질소 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 약물은 손쇱게 구할 수 있습니다. 사용하시기 바랍니다.
Osteoblast-derived oxysterol is a migration-inducing factor for human breast cancer cells.
물론 어느 약물이든 고단위로 사용하는 경우 가장 큰 문제는 내성입니다. 질소 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates) 약물은 한동안 효과적으로 작용하겠지만, 얼마 후 목표 암세포들이 반응을 멈춥니다. 단일약물을 고단위로 사용하는 것 보다는 상승효과가 있는 약물들을 낮은 단위로 복합 사용하는 것이 더 효과적이고 더 지속적이라는 단순한 논쟁이 가끔 무시되곤 합니다. 자연요법에서는 이때문에 좀더 효과적이고 지속적인 치료를 위해 몇가지 다른 기전의 성분들을 복합적으로 사용하는 것이 특징이지만 병원에서는 이러한 종류의 치료가 절대로 불가능합니다.
유전자 RhoA와 Ras를 억제하기 위해 자연치료제 조르반(Zorvan), 씨놀짐(SinnolZym) 정제와 액체, 지놀짐(GinolZym), 오랄짐(OralZym) 과 질소 비스포스포네이트(nitrogen bisphosphonates)와 루테올린(luteoli)을 추가적으로 사용한다면 금상첨화입니다. 플라보노이드(flavonoid)의 일종인 루테올린(luteolin)은 암 유전자 RhoA와 관련한 세포막의 합성을 매우 강력하게 억제하며, 세포증식 촉진인자 PI3K 및 혈관내피세포증식인자(VEGF)를 억제하여 암세포의 증식을 억제한다는 것이 밝혀졌습니다.
세포증식 촉진인자 PI3K가 억제될 때, 암세포의 증식과 항암치료, 방사선치료에서 내성을 만드는 핵심적 요인인 NF-kB가 활성화되지 못하고, 암세포는 자연사멸(apoptosis)하게 됩니다. 또한 암세포의 혈관형성을 다룬 연구에서는 RhoA와 특히 암세포와 관련된 생화학적 경로를 억제하는 능력을 확인할 수 있습니다. 만일 암 유전자 RhoA가 억제된다면, 암세포의 증식과 전이, 암종양 속으로 혈관이 형성되는 작용이 심각한 장애를 맞게 됩니다. 이것이 자연의 항암치료제가 만드는 작용입니다.
또한 루테올린(luteolin)은 세포주기(cell cycle)를 차단하여 분열을 억제하고, 대표적인 세포부착 물질인 카드헤린(E-cadherin) 단백의 발현을 조절하여 침윤(invasion)을 억제합니다. 특히 암 자연치료에서 기회가 날 때마다 강조하는 지방산합성에 관여하는 효소 FAS (fatty acid synthase)를 억제하는 작용은 말할 수 없이 중요합니다. 그러나 루테올린(luteolin)은 오히려 정상세포는 손상으로부터 보호하는 작용을 합니다. 더 이상 더 바랄 것이 있겠습니까?
Luteolin suppresses growth and migration of human lung cancer cells.
Luteolin enhances the bioavailability of benzo(a)pyrene in human colon carcinoma cells.
Luteolin inhibits protein kinase C(epsilon) and c-Src activities and UVB-induced skin cancer.
Luteolin inhibits invasion of prostate cancer PC3 cells through E-cadherin.
계속합니다.
ⓒ 저작권(copyright) 법에 의해 본 사이트(http://www.herbalzym.com)에 게시된 글은 보호받으므로 무단전재 및 재배포를 금지합니다. | 저작권문의는 herbalzym@hotmail.com 으로 하시기 바랍니다.