Apoptosis is a complex process, where important role is played by epigenetic mechanisms responsible for regulation of activity of proteins participating in this event. The presence of various forms of a given protein (as a result of alternative splicing) and post translation modification of protein molecules (phosphorylation, dephosphorylation, proteolytic cleavage) means that each protein can function as both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic factor. There are two major ways that could downregulate cancer cell apoptosis: (1) somatic and nonsomatic mutation and loss of expression of proapoptotic molecules; and (2) overexpression of apoptosis inhibitory molecules.
Some viruses associated with cancers use tricks to prevent apoptosis of the cells they have transformed. Several human papilloma viruses (HPV) have been implicated in causing cervical cancer. One of them produces a protein (E6) that binds and inactivates …
Mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation is one of the main sources for energy production, particularly at times of stress or fasting. Fatty acids are oxidized inside the mitochondrial matrix but the fatty acids to be oxidized come from the cytosol. Fatty acids are activated in the cytosol by esterification with Coenzyme A (CoA) to form acyl-CoA (RCO-CoA, where R is the fatty acid acyl group).
Activated medium-chain fatty acids (C8 fatty acid and C10 fatty acid) freely diffuse into mitochondria to be oxidized but long chain fatty acids do not diffuse into mitochondria so they must be transported in. Palmitoylcarnitine is a well-known intermediate in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. The transport of long chain fatty acids into mitochondria for oxidation is accomplished by the carnitine palmitoyltransferase system (CPTI and CPTII). CPTI exchanges …
It has long been known that calcium ions Ca(2+) signals govern a host of vital cell functions and so are necessary for cell survival. However, more recently it has become clear that cellular calcium ions Ca(2+) overload, or perturbation of intracellular Ca(2+) compartmentalization, can cause cytotoxicity and trigger either apoptotic or necrotic cell death.
Many cellular processes require proper cooperation between the plasma membrane, the nucleus and subcellular vesicular/tubular networks such as the ER (endoplasmic reticulum) and mitochondria. It has recently become clear that such contacts are crucial for the synthesis and intracellular transport of phospholipids as well as for intracellular Ca(2+) homeostasis, controlling fundamental processes like motility and contraction, secretion, cell growth, proliferation and apoptosis.
Altered metabolism is a feature of many diseases, as well as aging. The definition of this …
A number of recent anti-cancer strategies aim at targeting the mitochondrial apoptotic machinery to induce tumor cell death. Apoptosis is a form of cell death in which a programmed sequence of events leads to the elimination of cells. The term apoptosis is derived from the Greek word that signifies the dropping of leaves from the trees. Apoptosis plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining health by eliminating old cells, unnecessary cells, and unhealthy cells. The human body replaces perhaps a million cells a second. Too little or too much apoptosis plays a role in a great many diseases.
There is a distinct and precisely localized control over the fate of specific cells in a mixed cell population that undergo apoptosis. This event similar to proliferation is tightly regulated with both …
Cancer cells need a lot of nutrients to multiply and survive. While much is understood about how cancer cells use blood sugar to make energy, not much is known about how they get other nutrients. Two related pathways are involved in cancer growth:
The insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) signaling pathway, which is activated when nutrients are available,
The adenosine mono-phosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, activated when cells are starved for carbohydrates.
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. It is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia). The other means of maintaining blood glucose levels is through the degradation of …
Cancer was formerly believed to be a localized disease, characterized by a lesion, usually in the form of a growth, which appeared at some specific part of the body. This localized lesion was thought to be the result of activity produced by an invading virus, carcinogenic agent, or some form of trauma. Today, there is a growing conviction that cancer is a complex disease that is the end result of a disturbed metabolism. The frequent recurrence of a malignancy after treatment with the conventional methods of surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy results because the basic underlying metabolic cause of the cancer is rarely considered and consequently remains uncorrected.
In 2007, researchers at the University of Alberta, Canada, reported that DCA (dichloroacetate) has seemingly remarkable anticancer properties. DCA is a tiny molecule, odorless, …
Cancer cells are characterized by self-sufficiency in the absence of growth signals, their ability to evade apoptosis, resistance to anti-growth signals, sustained angiogenesis, uncontrolled proliferation, and invasion and metastasis. Alterations in cellular bioenergetics are an emerging hallmark of cancer.
Genome instability, leading to increased mutability, was considered the essential enabling characteristic for manifesting the hallmarks. However, the mutation rate for most genes is low making it unlikely that the numerous pathogenic mutations found in cancer cells would occur sporadically within a normal human lifespan. This then created a paradox. If mutations are such rare events, then how is it possible that cancer cells express so many different types and kinds of mutations? Mutations in each of cancer genes result in dysregulation of metabolic pathways involved in oxygen, iron, energy or nutrient …
 Phytosterols are plant-derived compounds structurally related to mammalian cell-derived cholesterol that function as essential constituents of plant cell membranes. Phytosterols are composed of 90% sterols and 10% stanols – and scientists maintain the plant ingredients lower cholesterol absorption in the small intestine by competing with it. Both classes of phytosterol are naturally occurring and can be found in a variety of medicinal plants and foods, including nuts, vegetable oils, seeds, and cereals.
Phytosterols are plant-derived compounds structurally related to mammalian cell-derived cholesterol that function as essential constituents of plant cell membranes. Phytosterols are composed of 90% sterols and 10% stanols – and scientists maintain the plant ingredients lower cholesterol absorption in the small intestine by competing with it. Both classes of phytosterol are naturally occurring and can be found in a variety of medicinal plants and foods, including nuts, vegetable oils, seeds, and cereals.
Phytosterols act through multiple mechanisms of action, including inhibition of carcinogen production, cancer-cell growth, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis, and through the promotion of apoptosis of cancer cells. In addition to altering cell-membrane structure and function, phytosterols promote apoptosis by lowering blood cholesterol levels.
Anticancer effects of phytosterols.…
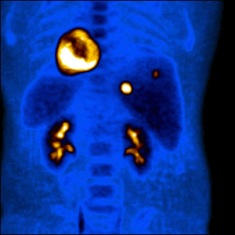 CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) is a type of protein molecule that can be found in many different cells of the body, but is typically associated with certain tumors and the developing fetus. The most frequent cancer which causes an increased CEA is cancer of the colon and rectum. CEA is most frequently tested in blood. It can also be tested in body fluids and in biopsy tissue. The best use of CEA is as a tumor marker, especially for cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. When the CEA level is abnormally high before surgery or other treatment, it is expected to fall to normal following successful surgery to remove all of the cancer. A rising CEA level indicates progression or recurrence of …
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) is a type of protein molecule that can be found in many different cells of the body, but is typically associated with certain tumors and the developing fetus. The most frequent cancer which causes an increased CEA is cancer of the colon and rectum. CEA is most frequently tested in blood. It can also be tested in body fluids and in biopsy tissue. The best use of CEA is as a tumor marker, especially for cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. When the CEA level is abnormally high before surgery or other treatment, it is expected to fall to normal following successful surgery to remove all of the cancer. A rising CEA level indicates progression or recurrence of …
Colon cancer claims 200,000 lives in Europe and the USA each year. With 300,000 new cases per year, it is the second commonest cancer and is therefore highly relevant to general medical practice. Surgical treatment is still a viable option in order to extend the patient’s life. Doctors can remove the section of the colon with the tumor and sew the healthier sections together. Freezing the tumor and removing it, also known as cryotherapy, is also a viable option. Surgery may also be an option to remove other infected body parts, depending on the size of the areas infected.
However, in most patients, there is no evidence of distant metastasis at the time of surgery, but the cancer has penetrated deeply into …