Flax is a blue flowering crop grown on the Prairies of Canada for its oil-rich seeds. There are two types of flax seed, yellow (or golden) and brown, and their nutritional profiles are very similar and both contain the same number of short-chain omega-3 fatty acids. While brown flax seed is edible for humans, it is more typically used in animal feeds because of its tougher texture. Golden flax seed is widely considered to be the best variety for human consumption. Canadian golden flax seed is grown primarily in the clean prairie provinces of Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Alberta. Canadian golden flax seed is some of the finest worldwide. …
FoxM1 (forkhead box protein M1) protein is a member of the Fox (forkhead box) family of transcription factors with known roles in regulating cell cycle progression. FOXM1 is a master regulator of cancer cell growth and is overexpressed in a majority of cancers, while its expression usually low in normal cells. Elevated FoxM1 expression is found in cancers of the liver, prostate, brain, breast, lung, colon, pancreas, skin, cervix, ovary, mouth, blood and nervous system. In addition, FoxM1 may drive tumor invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis. For these reasons, FoxM1 is an attractive target for anticancer drugs such as doxorubicin, epirubicin and cisplatin.
FoxM1 is a downstream component of Wnt signaling and is critical for β-catenin transcriptional function in tumor cells. Wnt3a increases the level and nuclear translocation of FoxM1, which binds …
Beta-catenin is a multifunctional oncogenic protein that contributes fundamentally to cell development and biology. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin has been implicated in many cancers, including colon cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer and endometrial cancer. β-catenin is an essential component of two cellular systems: As a component of the cadherin protein complex, β-catenin can regulate cell growth and adhesion between cells and also acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. The Wnt signaling pathway stimulates the growth of both normal cells and cancer stem cells.
Cytoplasmic β-catenin levels are normally kept low through continuous proteosome-mediated degradation by a ‘destructive complex’ of APC (adenomatous polyposis coli)/GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase-3β)/Axin. This is a feedback mechanism that prevents the excessive accumulation of β-catenin in …
In advanced stages of prostate cancer, it can metastasize to various regions of the body, most commonly the lymph nodes and bone. Tumor cell interaction with the surrounding microenvironment plays an important role in prostate cancer metastasis. Approximately 90% of patients with prostate cancer have bone metastasis at the time of death. Once prostate cancer cells spread to the bone, currently, no treatment regimens are available to eradicate the metastasis, and cancer-related death becomes inevitable. Thus, prostate cancer bone metastasis-associated clinical complications and treatment resistance pose major clinical challenges.
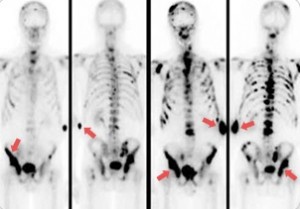 The bones that are most commonly involved are vertebrae, sternum, pelvic bones, ribs, and femurs. Metastatic prostate cancer cells tend to make the bones around them thicker and denser, whereas other …
The bones that are most commonly involved are vertebrae, sternum, pelvic bones, ribs, and femurs. Metastatic prostate cancer cells tend to make the bones around them thicker and denser, whereas other …
Lectins are carbohydrate (sugar)-binding proteins (not to be confused with glycoproteins, which are proteins containing sugar chains or residues). Lectins have been found in plant, viruses, microorganisms and animals. Lectins serve many different biological functions in animals, from the regulation of cell adhesion to glycoprotein synthesis and the control of protein levels in the blood. They have been classified according to their carbohydrate-binding specificity. They may also bind soluble extracellular and intercellular glycoproteins.
Carbohydrates are defined as organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that are organized into ring structures. Lectin-carbohydrate (cellular glycoconjugate) recognition is operative in biochemical information transfer. Changes in glycan structures and the interactions of these structures with endogenous carbohydrate-binding lectins are now considered to be potential biomarkers on cancer cells for monitoring tumor progression.
Tumor cells have …
Cancer cells are distinct from normal body cells based partly on their unique metabolic status, one element of which is an unusual requirement for fatty acid synthesis. Fatty acids are the major constituents of membrane lipid. Cellular proliferation requires fatty acids for synthesis of membranes and signaling molecules. Thus rapidly- proliferating cancer cells often have a robust program of fatty acid synthesis accompanied by high-level expression of associated genes such as fatty-acid synthase (FASN). FASN is over-expressed in many cancers. Increased lipid biosynthesis and desaturation are key requirements for tumor cell survival and proliferation.
Fatty acids are chains of carbons with attached hydrogen molecules at one end and an acid group (carboxylic acids) at the other end. Long-chain fatty acids are types of fats that have several carbons in their chain …