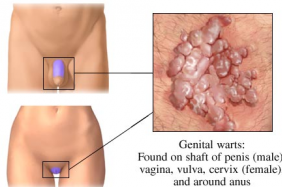
 All warts are caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) infections. HPV has over 100 different strains. Genital warts (condyloma acuminata) are the most common sexually transmitted disease and affect millions of people throughout the world. Genital warts appear as flesh-colored, round bumps of varying sizes. They can be smooth and flat or cauliflower-like with a small stalk. They can be seen on the labia, vagina, penis, scrotum, anus, skin around the anus, and uret
All warts are caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) infections. HPV has over 100 different strains. Genital warts (condyloma acuminata) are the most common sexually transmitted disease and affect millions of people throughout the world. Genital warts appear as flesh-colored, round bumps of varying sizes. They can be smooth and flat or cauliflower-like with a small stalk. They can be seen on the labia, vagina, penis, scrotum, anus, skin around the anus, and uret
HPV subtypes number 6 and 11 cause 97% of genital warts and are considered low risk because they very rarely will cause genital or anal cancer. On the other hand, HPV subtypes 16 and 18, for example, are considered high risk because, although they rarely cause genital warts, they can lead to cervical, anal or oral precancer and cancer.
What are the diseases induced by HPV?
| DISEASE | STRAIN |
| Common warts | 2, 7 |
| Plantar warts | 1, 2, 4 |
| Flat cutaneous warts | 3, 10 |
| Anogenital warts (Condyloma acuminatum) | 6, 11, 42, 43, 44, 55 and more |
| Genital malignancies | 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51 |
| Epidermodysplasia verruciformis | >15 strains |
| Focal epithjelial hyperplasia (oral) | 13, 32 |
| Oral Papillomas | 6, 7, 11, 16, 32 |
It is estimated that 75–80% of sexually active men and women will be infected with HPV at some point in their lives. HPV is spread by skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity; there does not need to be vaginal or anal intercourse to spread the infection. Most people who become infected with HPV will not have symptoms and will clear the infection on their own. For people who do develop genital warts, there are many options for treatment that your doctor may recommend. Some doctors will use podophyllin anti-mitotic solution and laser treatment.
Podophyllin resin is derived from the rhizome of the Mayapple, a plant that grows wild in eastern North America. In the United States, podophyllin is sold to physicians as a 10-25 percent suspension in tincture of benzoin. Podophyllin is an antimitotic agent that disrupts viral activity by inducing local tissue necrosis.The disadvantages to the use of podophyllin includes unstandardized preparation, side effects, lower effectiveness, failure to induce lasting remission, and teratogenicity. All of which are meant to remove the visible warts. . Some people will never get rid of it and will have it their entire life. Fortunately, HPV infection can be cleared by immune system modulator and enhancer known to natural medicine.
HPV can cause normal cells on infected skin to turn abnormal. Most of the time, you cannot see or feel these cell changes. HPV induced abnormal cells are interesting. In most cases, the body fights off HPV naturally and the infected cells then go back to normal. But in cases when the body does not fight off HPV, HPV can cause visible changes in the form of genital warts or cancer. Warts can appear within weeks or months after getting HPV. Cancer often takes years to develop after getting HPV. Cervical cancer is highly associated with HPV 16 and 18. 90% of cervical cancers contain HPV 16 and 18. The vulva, vagina, penis and anus also can be affected by these carcinogenic strains.
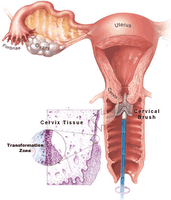 Pap smears detect abnormal cells which evince cervical dyplasia. In developing countries, where Pap smears are not available, rates of cervical cancer are really high. Pap smears detect abnormal cells which evince cervical dyplasia. The term “plasia” means growth. Cervical dysplasia means disordered growth and the appearance of abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix, the lowest part of the uterus. These changes in cervical tissue are classified as mild (CIN 1), moderate (CIN 2), or severe (CIN 3: the beginning stages of cancer). While dysplasia itself does not cause health problems, it is considered to be a precancerous condition. Left untreated, dysplasia sometimes progresses to an early form of cancer known as cervical carcinoma in situ, and eventually to invasive cervical cancer. For this reason, most physicians quickly remove suspicious cervical lesions and require frequent Pap smears to monitor for recurrences.
Pap smears detect abnormal cells which evince cervical dyplasia. In developing countries, where Pap smears are not available, rates of cervical cancer are really high. Pap smears detect abnormal cells which evince cervical dyplasia. The term “plasia” means growth. Cervical dysplasia means disordered growth and the appearance of abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix, the lowest part of the uterus. These changes in cervical tissue are classified as mild (CIN 1), moderate (CIN 2), or severe (CIN 3: the beginning stages of cancer). While dysplasia itself does not cause health problems, it is considered to be a precancerous condition. Left untreated, dysplasia sometimes progresses to an early form of cancer known as cervical carcinoma in situ, and eventually to invasive cervical cancer. For this reason, most physicians quickly remove suspicious cervical lesions and require frequent Pap smears to monitor for recurrences.
HPV and cervical cancer: updates on an established relationship.
Human papillomavirus infection and the primary and secondary prevention of cervical cancer.
However, HPV infection alone is not sufficient to induce malignant transformation, and other significant cofactors contribute to the multi-step process of tumor formation, such as individual genetic variations as well as environmental and immune factors. Women with weakened immunity are more likely to be infected with HPV and to have a persistent infection that does not resolve on its own. There is growing evidence that certain vitamins, such as vitamin A, B complex and D play a role in cervical health. A poor diet may also cause the immune system to weaken, decreasing the body’s ability to fight viruses such as HPV. Some research shows that women who use oral contraceptives may be at a higher risk for developing cervical dysplasia. However, it is not clear if the risk is directly attributable to the contraceptives themselves. One reason may be that oral contraceptives interfere with folic acid (also known as vitamin B9) metabolism in the cells around the cervix, and folic acid may help prevent or improve cervical dysplasia.
The folic acid is critical to synthesis of normal DNA as cells divide from one generation to the next. Cells that line the cervix replace themselves every 7-14 days and therefore, the cells must continuously form DNA as part of their genetic structure. Previous studies have demonstrated that poor folic acid status can lead to DNA abnormalities with subsequent development of cervical dysplasia or megaloblastic features of cervical cells (large abnormal cell appearance).
Oral contraceptives are known to increase the rate of cell division of cervical cells, hence, escalating the need for adequate folic acid intake. Studies demonstrated that folic acid supplementation could reverse cervical megaloblastic charges and cervical dysplasia, respectively, in patients using oral contraceptives. In fact, oral contraceptive use is a known risk factor for cervical dysplasia, primarily due to its effect on speeding up cell division rates.
Vitamins that might help are beta-carotene (vitamin A), folic acid as well as mineral selenium (sodium selenite), so you should make sure you are getting plenty of those. The vitamins do not cure the dysplasia but aid your immune system and help keep the cells from turning cancerous.
Retinoic acid activates interferon regulatory factor-1 gene expression in myeloid cells.
Regulation of cell growth and HPV genes by exogenous estrogen in cervical cancer cells.
Once infected with HPV, you are infected for life. There is no known cure and no medically-approved treatment. The best strategy is to modulate and enhance the immune system. Only the body’s immune system can eliminate the HPV infections. Modulation of antibody-mediated immune response by natural compounds is an attempt to improve and restore the body’s immune responses artificially.