Many scientists believe that microbes cause or contribute to between 15-25% of all cancers diagnosed worldwide each year. The frequency of liver cancer is high among Asians because liver cancer is closely linked to chronic hepatitis B infection. This is especially so in individuals who have been infected with chronic hepatitis B for most of their lives (it is usually a childhood disease). HBV infection is a serious clinical problem because of its worldwide distribution and potential adverse sequelae. Nearly 300 million persons in the world are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. High rates of chronic infection are found in some parts of Asia, Africa, the Pacific islands, South America, and the Middle East.
Although HBV can survive outside the body for up to 1 week—and therefore, might be transmitted …
Viruses are found wherever there is life and have probably existed since living cells first evolved. Most virus infections eventually result in the death of the host cell. Viral infections provoke an immune response that usually eliminates the infecting virus. However, some viruses including those causing AIDS, viral hepatitis, genital warts and cervical cancer evade these immune responses and result in chronic infections. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses. Viral populations do not grow through cell division, because they are acellular. Instead, they use the machinery and metabolism of a host cell to produce multiple copies of themselves, and they assemble in the cell.
Some viruses cause no apparent changes to the infected cell. Cells in which the virus is latent and inactive show few signs of infection and often function …
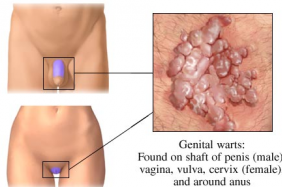 All warts are caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) infections. HPV has over 100 different strains. Genital warts (condyloma acuminata) are the most common sexually transmitted disease and affect millions of people throughout the world. Genital warts appear as flesh-colored, round bumps of varying sizes. They can be smooth and flat or cauliflower-like with a small stalk. They can be seen on the labia, vagina, penis, scrotum, anus, skin around the anus, and uret
All warts are caused by human papilloma virus (HPV) infections. HPV has over 100 different strains. Genital warts (condyloma acuminata) are the most common sexually transmitted disease and affect millions of people throughout the world. Genital warts appear as flesh-colored, round bumps of varying sizes. They can be smooth and flat or cauliflower-like with a small stalk. They can be seen on the labia, vagina, penis, scrotum, anus, skin around the anus, and uret
HPV subtypes number 6 and 11 cause 97% of genital warts and are considered low risk because they very rarely will cause genital or anal cancer. On the other hand, HPV subtypes 16 and 18, for example, are considered high risk because, although they rarely cause genital warts, they can lead …
The primary features of cancer are maintained via intrinsically modified metabolic activity, which is characterized by enhanced nutrient supply, energy production, and biosynthetic activity to synthesize a variety of macromolecular components during each passage through the cell cycle.
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid (building block of protein) in the body. Its main storage site is in the musculature; where about 60% of all the unbound amino acids are glutamine (glutamine makes up a smaller percentage of muscle protein, the main bound form). Glutamine has been called a “conditionally essential” nutrient, because it is non-essential in normal situations (meaning that the body can normally synthesize what it needs; not required in the diet), but in severe illness or injury becomes insufficient (there is then a need for supplementation from the …
It is only recently that a clear link has been established between stem cells and cancer in a variety of cancer types since cancers often arise from the transformation of normal stem cells. In solid organs, cancer stem cells create all the cells in the tumors. But in blood cancers they create havoc in the circulatory and immune systems by spawning large numbers of immature or abnormal cells (usually white blood cells).
For example, in leukemia, these abnormal cells pool in the bone marrow and displace healthy cells, attack or overwhelm the immune system, or cause a platelet or red blood cell deficiency leading to poor wound healing or anemia. Because a stem cell always retains a “copy” of itself in the process of cell division, the leukemia stem cell has …
There are two main categories of lung cancer.
1. Non–small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): About 85 to 87% of lung cancers are in this category. This cancer grows more slowly than small cell lung carcinoma. Nevertheless, by the time about 40% of people are diagnosed, the cancer has spread to other parts of the body outside of the chest.
There are 3 sub-types of NSCLC. The cells in these sub-types differ in size, shape, and chemical make-up.
Squamous cell carcinoma: About 25% to 30% of all lung cancers are this kind. They are linked to smoking and tend to be found in the middle of the lungs, near a bronchus.
Adenocarcinoma: This type accounts for about 40% of lung cancers. It is usually found in the outer part of the lung.
Large-cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma: …
The war on cancer, fought for four decades marked by failure and frustration. We’ve learned enormous amounts about the disease, but it hasn’t translated into therapy. This is especially true in cancer, where old and new targeted therapies continue to fail and the most recent ones do not offer much improvement on clinical outcome parameters. New drugs are continuously designed and tried, it seems inevitable that genetic and signal protein targets pose too broad flexibility and variability, often changing target characteristics and thus escape treatments turning “magic bullets” into rather “wondering bullets”.
Metabolic modulation may be a viable therapeutic approach in the treatment of cancer and leukemia. Metabolic targeted therapies are aimed at control points of the metabolic network by targeting particular enzymes of major macromolecule synthesis pathways in cancer and …